Ectopic pregnancy management is a critical aspect of emergency obstetric care. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus—most commonly in the fallopian tube. This condition is life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated promptly. Early detection and appropriate management help prevent complications, preserve fertility, and reduce maternal mortality.
This comprehensive guide explains symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, recovery, fertility outcomes, and prevention strategies for ectopic pregnancy.
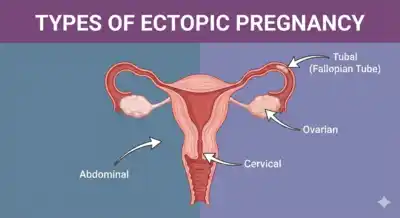
- What Is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
- Causes & Risk Factors
- Early & Emergency Symptoms
- Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
- Ectopic Pregnancy Management Options
- Medical Management (Methotrexate)
- Surgical Management
- Emergency & Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
- Recovery & Follow-Up Care
- Future Fertility & Pregnancy
- Can Ectopic Pregnancy Be Prevented?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Featured Snippet:
Ectopic pregnancy management depends on early diagnosis and includes medical treatment with methotrexate, minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery, or emergency surgery in case of rupture. Prompt care is essential to prevent life-threatening complications.
What Is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity. Over 90% occur in the fallopian tubes, but implantation can also happen in the ovary, cervix, or abdominal cavity. Since these locations cannot support a growing pregnancy, early treatment is mandatory.
Causes & Risk Factors
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Tubal surgery or sterilization
- Assisted reproductive techniques (IVF)
- Smoking
- Endometriosis
- History of sexually transmitted infections
Early & Emergency Symptoms
Early symptoms often mimic normal pregnancy, which makes diagnosis challenging.
Early symptoms:
- Missed periods
- Lower abdominal pain
- Light vaginal bleeding
- Nausea or breast tenderness
Emergency symptoms (ruptured ectopic pregnancy):
- Sudden severe abdominal pain
- Shoulder pain
- Dizziness or fainting
- Heavy internal bleeding
- Low blood pressure
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Timely diagnosis is essential for safe ectopic pregnancy management.
- Pregnancy test: Positive urine or blood test
- Serial beta-hCG levels: Abnormally rising levels
- Transvaginal ultrasound: Absence of intrauterine pregnancy
- Pelvic examination: Cervical motion tenderness or adnexal mass
Ectopic Pregnancy Management Options
The choice of treatment depends on gestational age, hCG levels, ultrasound findings, and patient stability.
- Expectant management (selected cases)
- Medical management
- Surgical management
laparoscopic gynecological procedure
Medical Management (Methotrexate)
Methotrexate is a chemotherapy drug used to stop pregnancy tissue growth in early ectopic pregnancies.
Eligibility criteria:
- Stable patient
- Low beta-hCG levels
- No fetal cardiac activity
- No tubal rupture
Advantages:
- Non-surgical
- Preserves fallopian tube
- Lower cost
Side effects:
- Nausea
- Mouth ulcers
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue
Surgical Management
Surgery is recommended when medical therapy fails or is contraindicated.
Types of surgery:
- Laparoscopic salpingostomy: Removal of ectopic tissue while preserving tube
- Laparoscopic salpingectomy: Removal of affected tube
- Laparotomy: Open surgery in emergencies
Emergency & Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
A ruptured ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency requiring immediate surgery and blood transfusion. Delayed treatment can lead to severe hemorrhage and maternal death.
Recovery & Follow-Up Care
- Regular beta-hCG monitoring until negative
- Avoid pregnancy for 3–6 months
- Emotional support and counseling
- Follow-up ultrasound if required
Future Fertility & Pregnancy
Most women can conceive again after ectopic pregnancy management. Fertility depends on tubal health, type of treatment, and underlying conditions.
- Natural conception is possible
- IVF may be advised in damaged tubes
- Early ultrasound is mandatory in next pregnancy
Can Ectopic Pregnancy Be Prevented?
While not always preventable, risk can be reduced by:
- Treating pelvic infections early
- Avoiding smoking
- Early pregnancy evaluation
- Safe sexual practices
Frequently Asked Questions
Is ectopic pregnancy life-threatening?
Yes. Without timely ectopic pregnancy management, it can cause severe internal bleeding and death.
Can ectopic pregnancy survive?
No. An ectopic pregnancy cannot develop into a viable baby.
How soon can I get pregnant again?
Doctors usually advise waiting 3–6 months after treatment.
Does methotrexate affect future fertility?
No, methotrexate does not reduce long-term fertility when used correctly.
Can ectopic pregnancy happen again?
Yes. Risk increases after one ectopic pregnancy, so early monitoring is essential.
Authoritative Video Links
These videos feature qualified medical professionals providing overviews and clinical guidance on the topic:
| Source | Description | Link |
| Stanford Medicine | A comprehensive explanation by Dr. Kate Shaw, Chief of Gynecology and Gynecologic Specialties at Stanford, covering risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options. | What is an ectopic pregnancy? Doctor explains risk factors, symptoms, & treatment |