Irregular Periods: Causes & Treatment Options
Irregular periods are one of the most common gynecological concerns affecting women of all ages. While occasional cycle changes can be normal, persistent irregularity may signal an underlying hormonal, lifestyle, or medical condition that needs attention.
This comprehensive guide explains why periods become irregular, how they are diagnosed, and the most effective treatment options—from lifestyle changes to medical care.
Quick Answer: Irregular periods occur when the menstrual cycle varies in length, flow, or timing due to hormonal imbalance, stress, PCOS, thyroid disorders, weight changes, or medical conditions. Treatment depends on the cause and may include lifestyle changes, hormone therapy, or medical management.
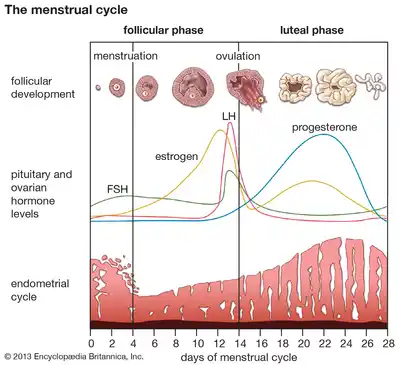
Table of Contents
- What Are Irregular Periods?
- What Is a Normal Menstrual Cycle?
- Common Causes of Irregular Periods
- Symptoms to Watch For
- How Irregular Periods Are Diagnosed
- Treatment Options for Irregular Periods
- Lifestyle & Home Remedies
- When to See a Gynecologist
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Irregular Periods?
Irregular periods refer to menstrual cycles that are inconsistent in length, timing, or flow. This may include:
- Cycles shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days
- Missed periods (amenorrhea)
- Heavy or very light bleeding
- Spotting between periods
What Is a Normal Menstrual Cycle?
A normal menstrual cycle lasts between 21–35 days, with bleeding for 3–7 days. Ovulation typically occurs mid-cycle, regulated by estrogen and progesterone.
Common Causes of Irregular Periods
1. Hormonal Imbalance
Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone can disrupt ovulation, leading to cycle irregularity.
2. PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
PCOS is one of the leading causes of irregular periods, associated with insulin resistance, weight gain, acne, and excess hair growth.
3. Thyroid Disorders
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can affect menstrual regularity.
4. Stress & Lifestyle Factors
Chronic stress, poor sleep, extreme exercise, or sudden weight changes can delay or stop ovulation.
5. Perimenopause
Women in their 40s may experience cycle changes as ovarian function declines.
6. Medical Conditions
- Endometriosis
- Uterine fibroids
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Symptoms to Watch For
- Missed or delayed periods
- Very heavy bleeding or clots
- Severe menstrual pain
- Unpredictable cycles
- Difficulty conceiving
How Irregular Periods Are Diagnosed
Your gynecologist may recommend:
- Detailed menstrual history
- Blood tests (hormones, thyroid, prolactin)
- Pelvic ultrasound
- PCOS screening
Treatment Options for Irregular Periods
Medical Treatments
- Hormonal therapy (oral contraceptives or progesterone)
- Thyroid medication
- Insulin-sensitizing drugs for PCOS
- Treatment of underlying conditions
Fertility-Focused Treatment
Ovulation-inducing medications may be advised for women trying to conceive.
Lifestyle & Home Remedies
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Balanced diet rich in iron and vitamins
- Regular physical activity
- Stress management (yoga, meditation)
- Adequate sleep
When to See a Gynecologist
Consult a doctor if:
- You miss periods for 3 months
- Bleeding is excessively heavy or painful
- Periods stop suddenly
- You are trying to conceive without success
Trusted Medical References:
- Office on Women’s Health (HHS): Period Problems
- Office on Women’s Health (HHS): Period Problems
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can stress cause irregular periods?
Yes. Stress affects the hypothalamus, which controls hormone release, potentially delaying ovulation.
2. Are irregular periods dangerous?
Occasional irregularity is common, but persistent irregular periods require evaluation to rule out underlying conditions.
3. Can irregular periods be treated naturally?
Mild irregularity may improve with lifestyle changes, but medical evaluation is essential for persistent issues.
4. Do irregular periods affect fertility?
Yes, especially if ovulation is inconsistent. Proper treatment can significantly improve fertility outcomes.